
由于我 前几天写的文章前几天写的文章 中提到了 一加 6 如何启用 KernelSU。后经过本人测试,如果使用 kprobe 集成的方法编译出的内核会无法启动,而 kernelSU 官网中提到的手动修改源代码的方法编译出的内核会无法使用模块。所以干脆记录一下我的修改和编译过程。
理论上开源了的内核都可以用这个方法,尽量不要使用和系统不匹配的内核。
本文的方法不用编译整个安卓系统,仅编译内核。使用 GitHub Action 的方式编译,整个过程在 20 分钟之内。
一、拉取 PixelExperience 的内核源码
1、Fork 内核仓库
由于 PixelExperience 开源了内核,所以直接 fork 到自己的仓库即可。
https://github.com/PixelExperience-Devices/kernel_oneplus_sdm845
当然你也尝试选择 LineageOS 的内核:https://github.com/LineageOS/android_kernel_oneplus_sdm845
2、分支相关设置和说明(可选)
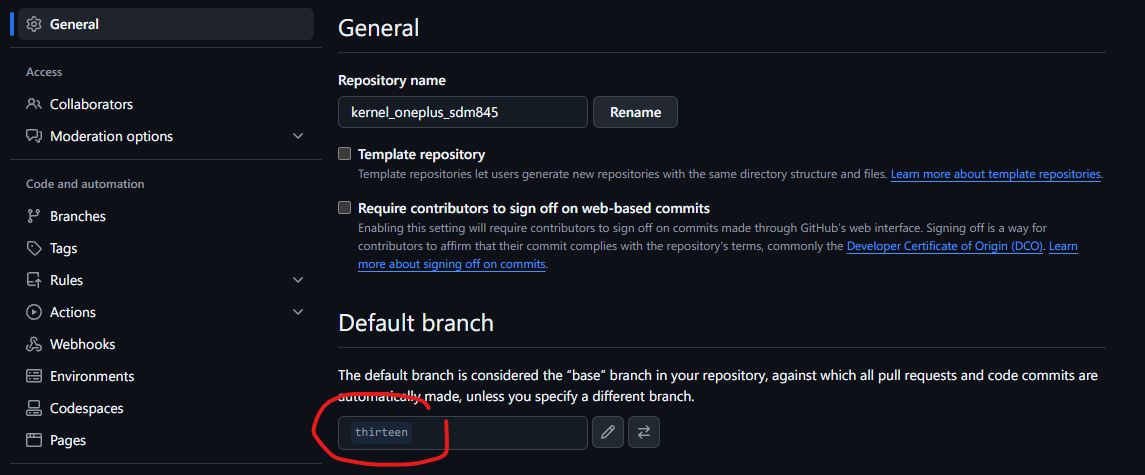
设置默认分支
由于 PixelExperience 官网中最后支持 OnePlus 6 的系统版本是 Android 13 ,并且手机也用的是 Android 13,所以可以设置默认分支为 thirteen。
其中 thirteen-wip 分支中的 wip 一般代表 work in progress
删除不需要的分支
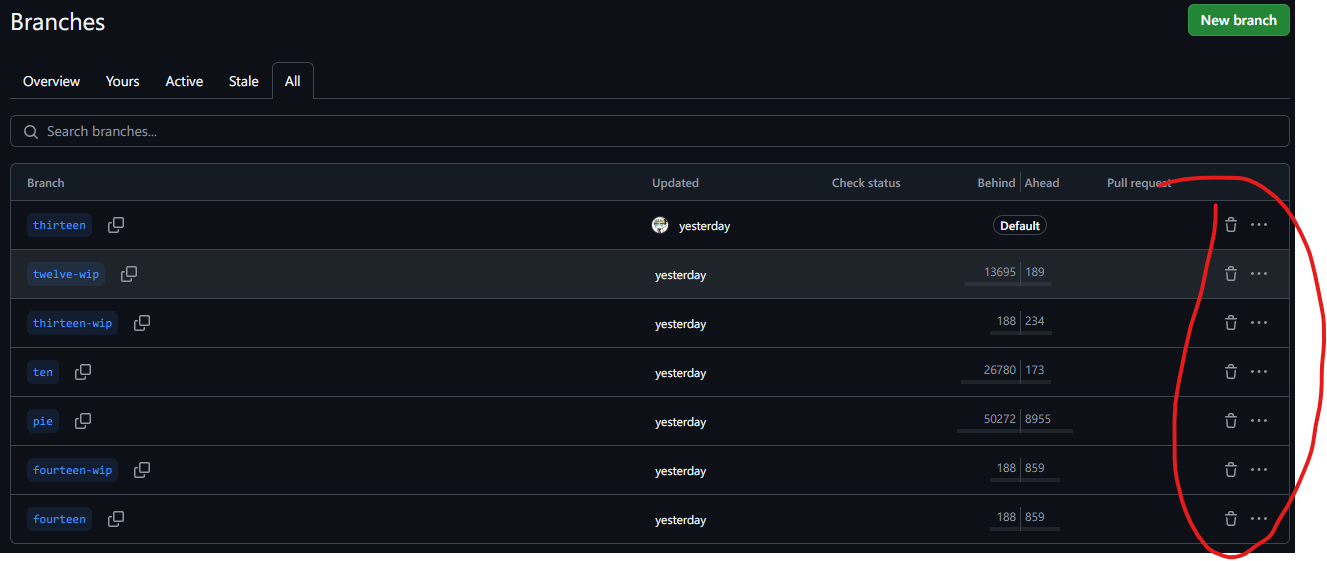
理由同上,只用保留 thirteen 和 thirteen-wip 这两个分支。
3、clone 到本地
在你想要的目录下运行:
git clone -b thirteen --depth 1 https://xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
使用 -depth 1 选项仅拉取最近一次提交,不然下载的会很大。
二、手动修改源码
你可以使用喜欢的编译器来修改代码,比如 VSCode 或者 Vim。
1、将 KernelSU 添加到源码树
进入你的源码目录
cd xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
使用以下命令下载相关文件和修改对应设置(官网提供)
curl -LSs "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tiann/KernelSU/main/kernel/setup.sh" | bash -s v0.9.5
非 GKI 设备官网支持到 v0.9.5,所以这里会下载 KernelSU(v0.9.5)
如果没有出错,会自动下载 KernelSU 到源码目录,并且修改了如下文件:
drivers/Kconfig:
source "drivers/oneplus/Kconfig"+source "drivers/kernelsu/Kconfig"endmenu
drivers/Makefile:
obj-$(CONFIG_SENSORS_SSC) += sensors/obj-$(CONFIG_TEE) += tee/obj-y += oneplus/++obj-$(CONFIG_KSU) += kernelsu/
drivers/kernelsu:
+../KernelSU/kernel
2、修改对应的内核配置文件
内核配置文件 .config 中存放着一些参数的配置。选择对应手机的型号添加 kernleSU 的参数。
一般配置文件在 arch/arm64/configs 或者 arch/arm64/configs/vendor 中。
Oneplus 6 的代号是 enchilada 所以选择 arch/arm64/configs/enchilada_defconfig
CONFIG_LZ4_COMPRESS=yCONFIG_LZ4_DECOMPRESS=yCONFIG_DECOMPRESS_LZ4=y++# KernelSU+CONFIG_KSU=y
3、添加 KernelSU 的调用
主要是要改四个地方,更详细的可以看我的这次提交 Commit 465796c
- faccessat,通常位于 fs/open.c
@@ -354,22 +354,31 @@
}
return error;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
extern int ksu_handle_faccessat(int *dfd, const char __user **filename_user, int *mode,
int *flags);
#endif
/*
* access() needs to use the real uid/gid, not the effective uid/gid.
* We do this by temporarily clearing all FS-related capabilities and
* switching the fsuid/fsgid around to the real ones.
*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(faccessat, int, dfd, const char __user *, filename, int, mode)
{
const struct cred *old_cred;
struct cred *override_cred;
struct path path;
struct inode *inode;
struct vfsmount *mnt;
int res;
unsigned int lookup_flags = LOOKUP_FOLLOW;
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
ksu_handle_faccessat(&dfd, &filename, &mode, NULL);
#endif
if (mode & ~S_IRWXO) /* where's F_OK, X_OK, W_OK, R_OK? */
return -EINVAL;
- do_execveat_common,通常位于 fs/exec.c
@@ -1675,18 +1675,34 @@
/*
* sys_execve() executes a new program.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
extern bool ksu_execveat_hook __read_mostly;
extern int ksu_handle_execveat(int *fd, struct filename **filename_ptr, void *argv,
void *envp, int *flags);
extern int ksu_handle_execveat_sucompat(int *fd, struct filename **filename_ptr,
void *argv, void *envp, int *flags);
#endif
static int do_execveat_common(int fd, struct filename *filename,
struct user_arg_ptr argv,
struct user_arg_ptr envp,
int flags)
{
char *pathbuf = NULL;
struct linux_binprm *bprm;
struct file *file;
struct files_struct *displaced;
int retval;
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
if (unlikely(ksu_execveat_hook))
ksu_handle_execveat(&fd, &filename, &argv, &envp, &flags);
else
ksu_handle_execveat_sucompat(&fd, &filename, &argv, &envp, &flags);
#endif
if (IS_ERR(filename))
return PTR_ERR(filename);
- vfs_read,通常位于 fs/read_write.c
@@ -456,10 +456,21 @@ ssize_t __vfs_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count,
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__vfs_read);
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
extern bool ksu_vfs_read_hook __read_mostly;
extern int ksu_handle_vfs_read(struct file **file_ptr, char __user **buf_ptr,
size_t *count_ptr, loff_t **pos);
#endif
ssize_t vfs_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
ssize_t ret;
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
if (unlikely(ksu_vfs_read_hook))
ksu_handle_vfs_read(&file, &buf, &count, &pos);
#endif
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_READ))
return -EBADF;
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_CAN_READ))
- vfs_fstatat,通常位于 fs/stat.c
@@ -87,13 +87,21 @@ int vfs_fstat(unsigned int fd, struct kstat *stat)
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(vfs_fstat);
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
extern int ksu_handle_stat(int *dfd, const char __user **filename_user, int *flags);
#endif
int vfs_fstatat(int dfd, const char __user *filename, struct kstat *stat,
int flag)
{
struct path path;
int error = -EINVAL;
unsigned int lookup_flags = 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
ksu_handle_stat(&dfd, &filename, &flag);
#endif
if ((flag & ~(AT_SYMLINK_NOFOLLOW | AT_NO_AUTOMOUNT |
AT_EMPTY_PATH)) != 0)
goto out;
4、其他建议的修改
开启安全模式 drivers/input/input.c:
@@ -377,11 +377,21 @@ static int input_get_disposition(struct input_dev *dev,
return disposition;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
extern bool ksu_input_hook __read_mostly;
extern int ksu_handle_input_handle_event(unsigned int *type, unsigned int *code, int *value);
#endif
static void input_handle_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
int disposition = input_get_disposition(dev, type, code, &value);
#ifdef CONFIG_KSU
if (unlikely(ksu_input_hook))
ksu_handle_input_handle_event(&type, &code, &value);
#endif
if (disposition != INPUT_IGNORE_EVENT && type != EV_SYN)
add_input_randomness(type, code, value);
pm fs/devpts/inode.c:
@@ -548,25 +548,28 @@
dentry = d_alloc_name(root, s);
if (dentry) {
dentry->d_fsdata = priv;
d_add(dentry, inode);
fsnotify_create(d_inode(root), dentry);
} else {
iput(inode);
dentry = ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
}
return dentry;
}
extern int ksu_handle_devpts(struct inode*);
/**
* devpts_get_priv -- get private data for a slave
* @pts_inode: inode of the slave
*
* Returns whatever was passed as priv in devpts_pty_new for a given inode.
*/
void *devpts_get_priv(struct dentry *dentry)
{
ksu_handle_devpts(dentry->d_inode);
if (dentry->d_sb->s_magic != DEVPTS_SUPER_MAGIC)
return NULL;
return dentry->d_fsdata;
path_umount fs/namespace.c:
@@ -1711,6 +1711,40 @@ static inline bool may_mandlock(void)
}
#endif
static int can_umount(const struct path *path, int flags)
{
struct mount *mnt = real_mount(path->mnt);
if (flags & ~(MNT_FORCE | MNT_DETACH | MNT_EXPIRE | UMOUNT_NOFOLLOW))
return -EINVAL;
if (!may_mount())
return -EPERM;
if (path->dentry != path->mnt->mnt_root)
return -EINVAL;
if (!check_mnt(mnt))
return -EINVAL;
if (mnt->mnt.mnt_flags & MNT_LOCKED) /* Check optimistically */
return -EINVAL;
if (flags & MNT_FORCE && !capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return -EPERM;
return 0;
}
int path_umount(struct path *path, int flags)
{
struct mount *mnt = real_mount(path->mnt);
int ret;
ret = can_umount(path, flags);
if (!ret)
ret = do_umount(mnt, flags);
/* we mustn't call path_put() as that would clear mnt_expiry_mark */
dput(path->dentry);
mntput_no_expire(mnt);
return ret;
}
/*
* Now umount can handle mount points as well as block devices.
* This is important for filesystems which use unnamed block devices.
修改完所有代码后建议提交到远程。
三、编译并刷入内核
一共有两种方法,建议尝试第二种
1、本地编译(不推荐)
修改好代码后就可以编译内核了
make ARCH=arm64 O=out enchilada_defconfig
make ARCH=arm64 -j$(nproc) O=out
然后将编译出来的 Image.gz-dtb 通过 Anykernel3 制作成刷机包,通过 adb sideload 的方式刷入手机重启即可。
2、利用 GitHub Action
使用安卓内核编译模板,我选择的是 kernelSU_Action
如果全部是按照本文修改的话,配置文件只用改这几行
KERNEL_SOURCE=https://github.com/用户名/kernel_oneplus_sdm845
KERNEL_SOURCE_BRANCH=thirteen
KERNEL_CONFIG=enchilada_defconfig
SOURCE_BOOT_IMAGE=你提取的 boot.img 直链
然后开一个 Action 等待构建完成,我的构建时间如下:
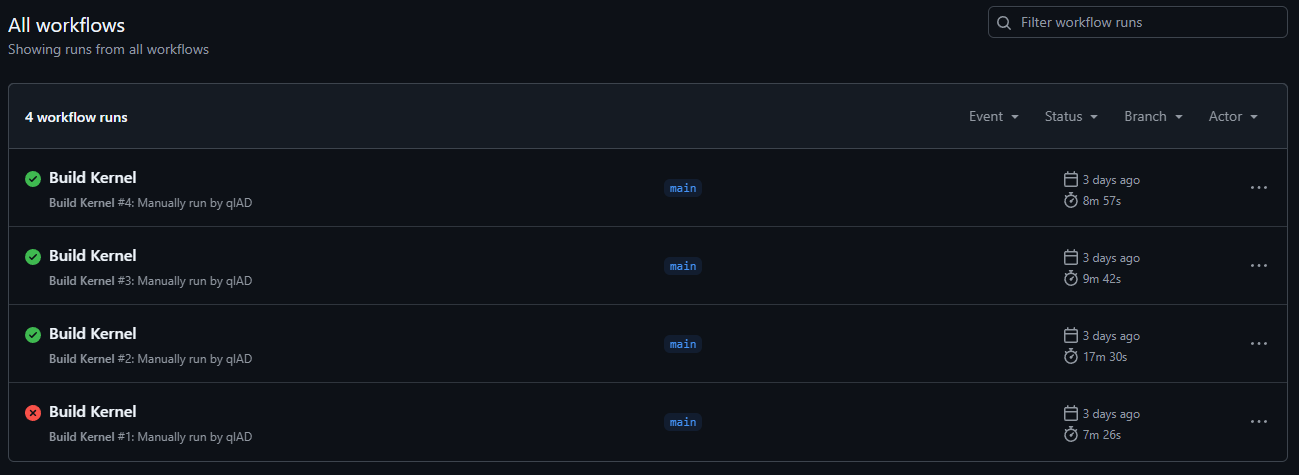
构建完成只会会自动打包 Anykernel3.zip
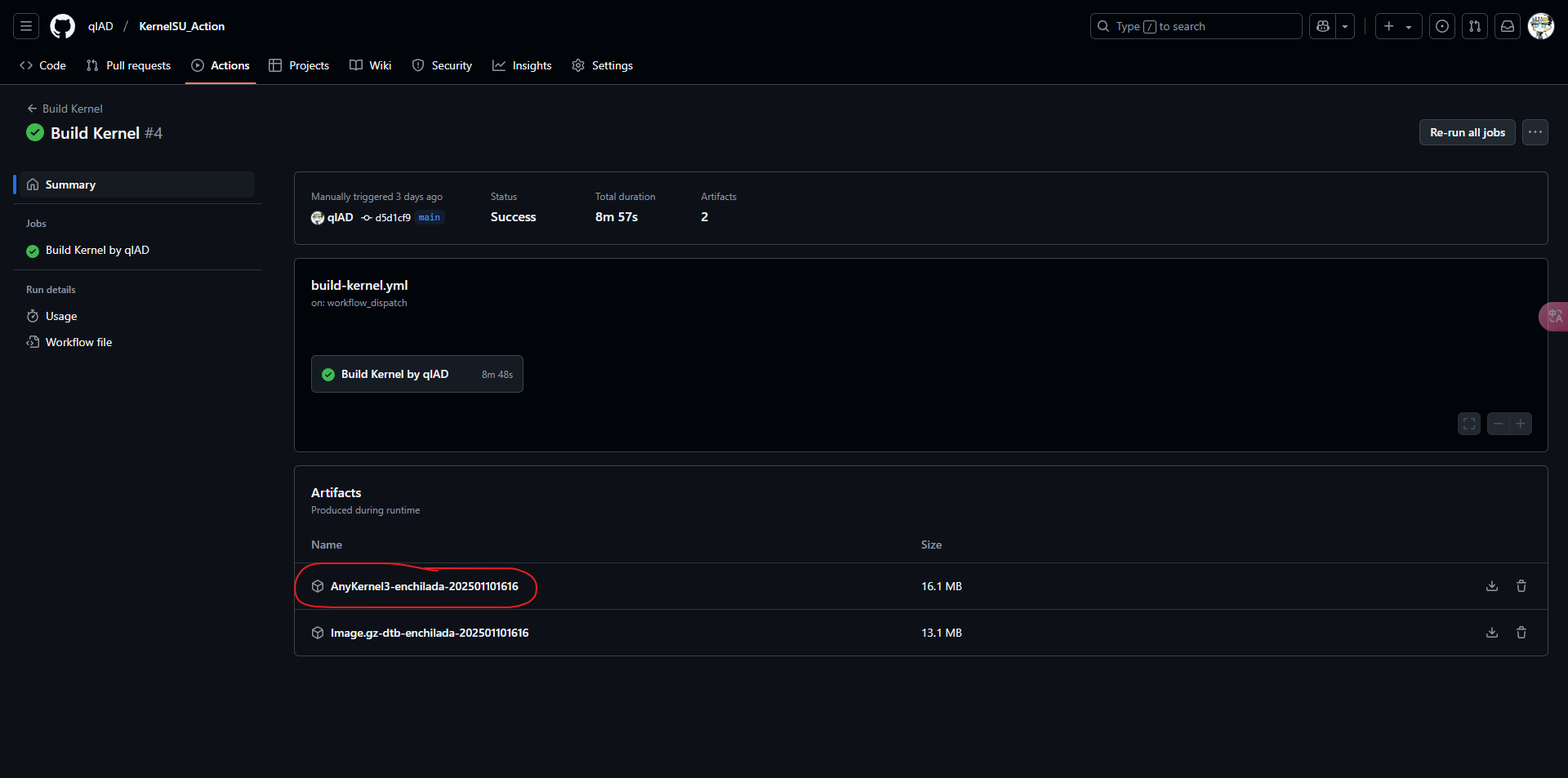
下载到电脑然后通过 adb sideload Anykernel3-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.zip 刷入重启即可
四、一些问题
通过上面的内容,你编译的内核就可以直接用了,KernelSU 也显示工作中。那么以下就是途中可能会遇到的一些问题。
1、当前 KernelSU 版本 16 过低
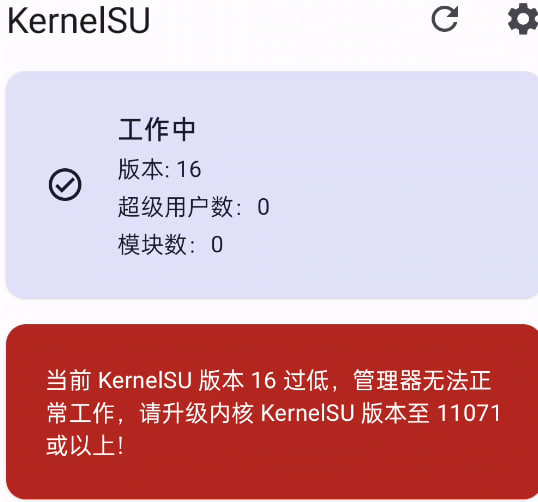
来源:#issues/1210
解决方案:将你的 KernelSU 文件夹作为 git 子模块使用,然后再重新编译
2、模块按钮无法使用
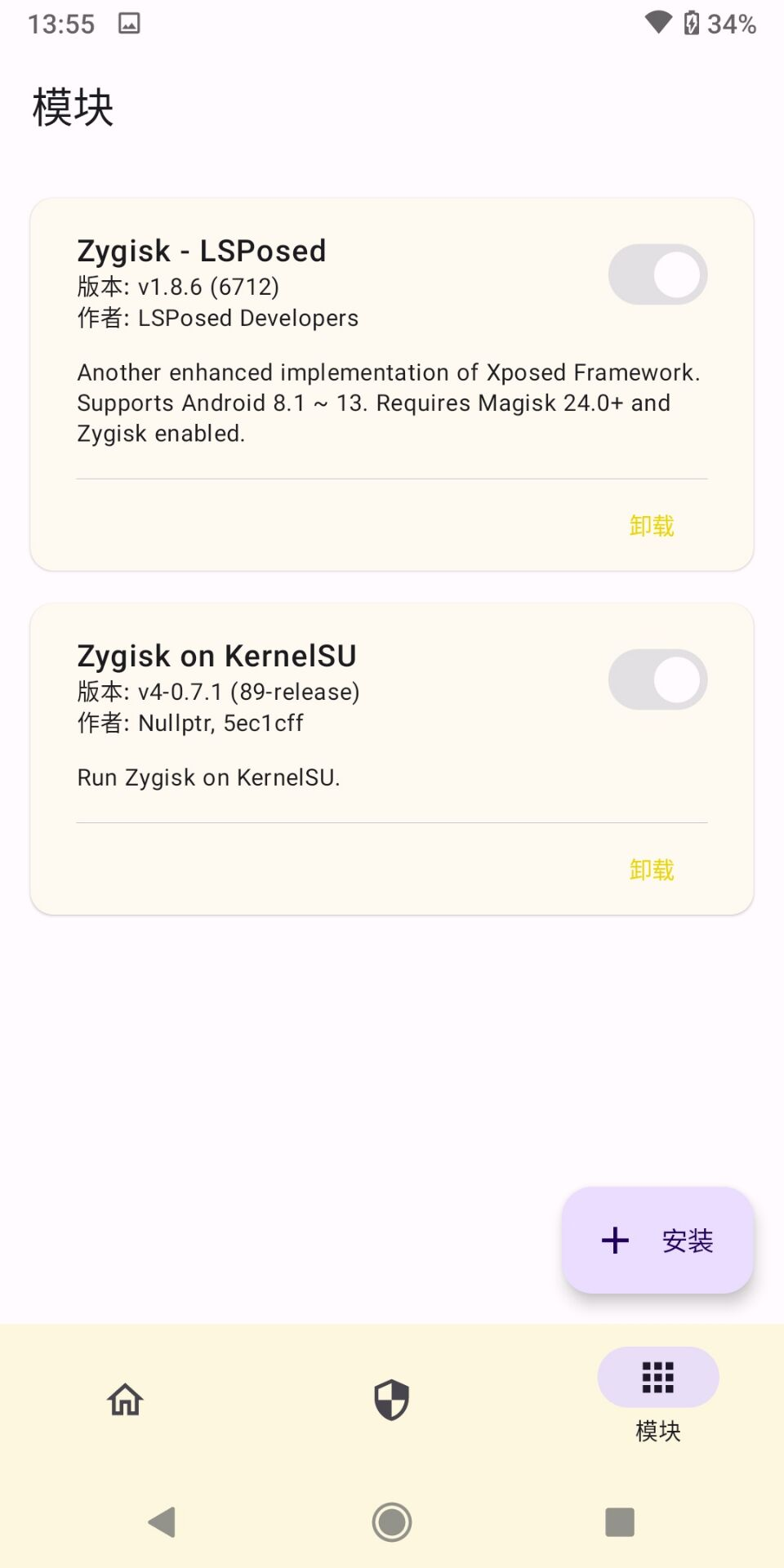
来源:#issues/824
解决方案:见这次提交 Commit d959a55 修改 selinux 相关代码